Tutorials
- USER GUIDES & VIDEO TUTORIALS
- ALL VIDEO TUTORIALS
- OVERVIEW
- ASSETS
- CREATE COURSE
- Getting Started with Creating Courses
- Create Course - Course Settings
- Course Builder (TOC)
- Build Lessons
- Tool Settings
- Advanced Tab – An Overview
- Typography
- Borders
- Style and Spacing
- Colors
- Advanced Techniques
- Responsive Design
- Move or Resize Settings Panel
- Row Effects
- MANAGE COURSES
- MANAGE TEMPLATES
- MANAGE XAPI
- ADMIN
- ACCOUNT
Colors
Table of Contents
COLORS
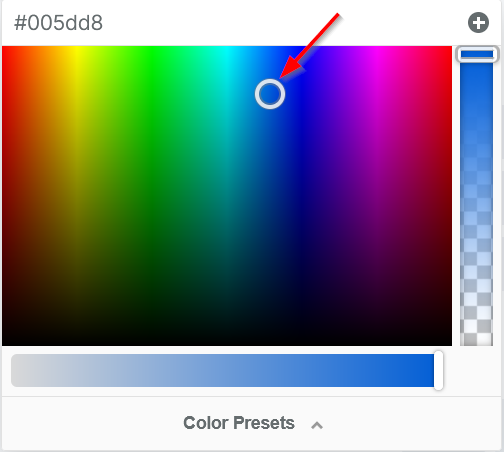
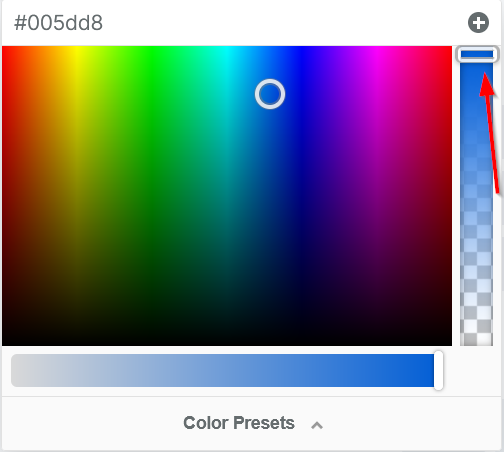
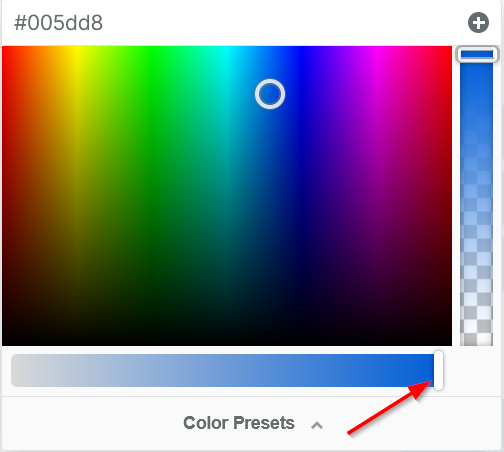
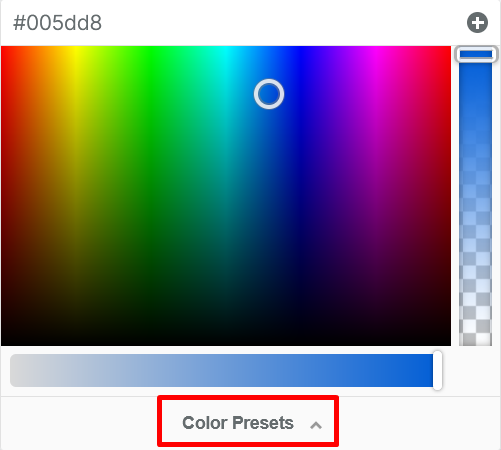
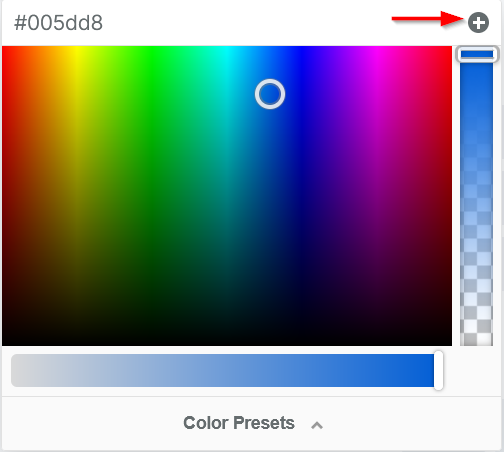
When adding color to your text, icons, buttons, borders, text shadows, and more, the color picker (or color dropper) allows you to easily customize and select from a wide range of colors.
COLOR PICKER
To adjust the color setting for any page element or tool, click the color picker icon from the settings panel: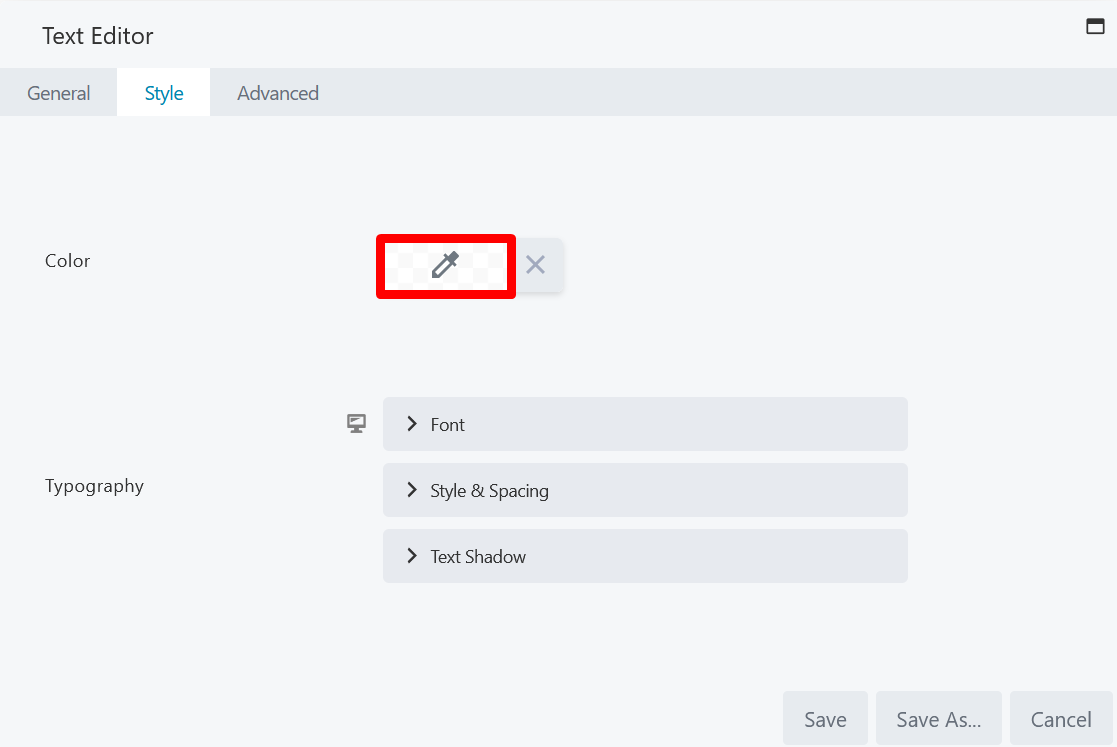
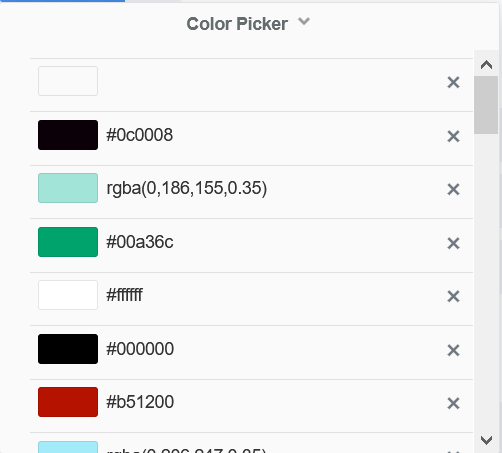
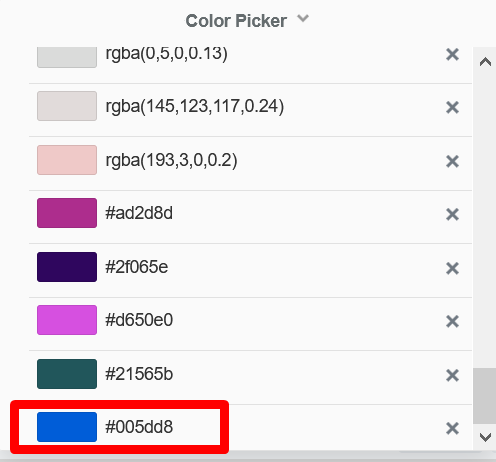
COLOR PRESETS
Color presets are any saved colors in your palette, which can include default system colors and any custom colors you have opted to save:
COLOR GRADIENTS FOR ROW AND COLUMN BACKGROUNDS AND OVERLAYS
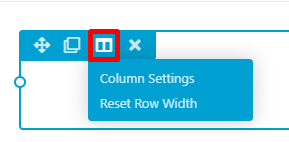
A color gradient is a style in which the selected color is lighter on top and darker on the bottom. When adding rows or columns to your lesson pages, you can add color gradients to the background to increase visual interest to your page. To add a gradient to your column, hover over your desired column, click the Edit Column option, then select COLUMN SETTINGS:
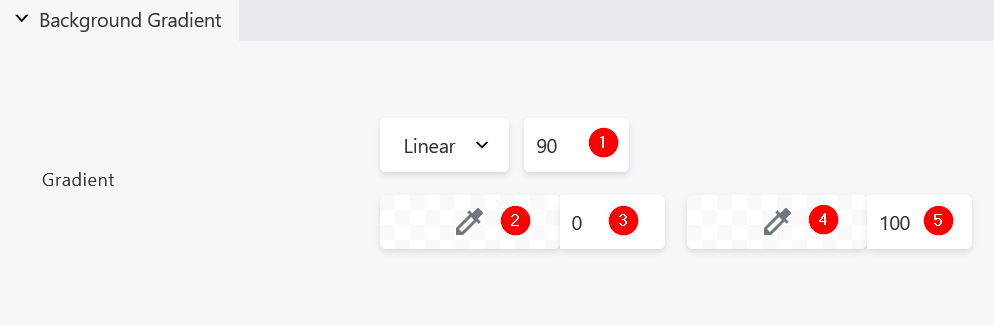
- Adjust the gradient angle
- Select the first color for your gradient
- Select the first color stop
- Select the second color for your gradient
- Select the second color stop
 The color stop defines where the gradient starts and stops on the gradient line.
The color stop defines where the gradient starts and stops on the gradient line.
- A linear gradient, set to an angle of 0, with the first color stop at 0% and the second color stop at 100%:

- A linear gradient, set to an angle of 180, with the first color stop at 0% and the second color stop at 100%:

- A linear gradient, set to an angle of 90, with the first color stop at 30% and the second color stop at 70%:

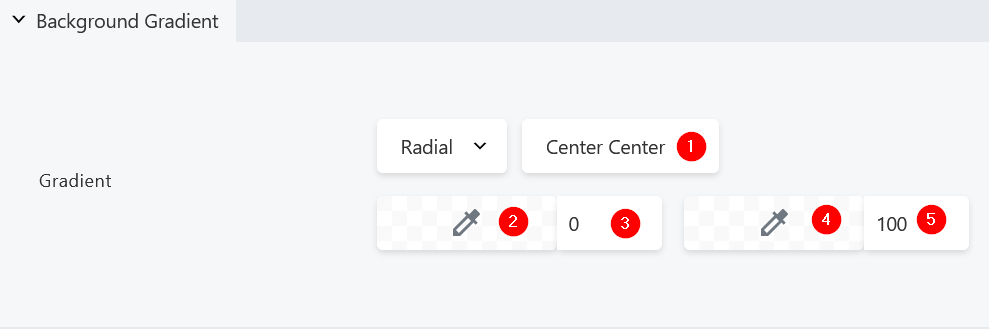
- Adjust the gradient locus
- Adjust the gradient locus
- Select the first color stop
- Select the second color for your gradient
- Select the second color stop
- A radial gradient, set to a locus of Center Center, with the first color stop at 0% and the second color stop at 100%:

- A radial gradient, set to a locus of Center Center, with the first color stop at 30% and the second color stop at 80%:

- A radial gradient, set to a locus of Left Top, with the first color stop at 0% and the second color stop at 100%:

- A radial gradient, set to a locus of Left Top, with the first color stop at 30% and the second color stop at 80%:

